Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
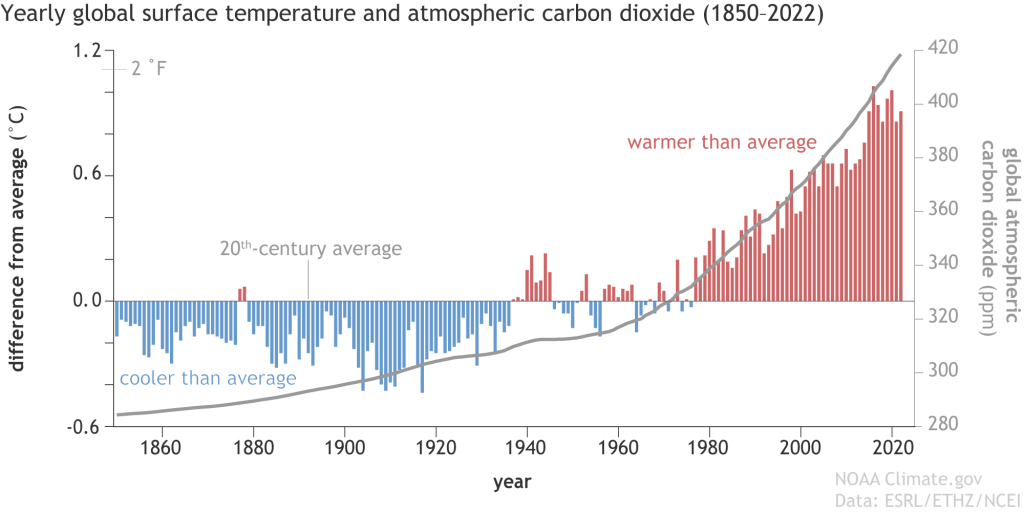 |  |
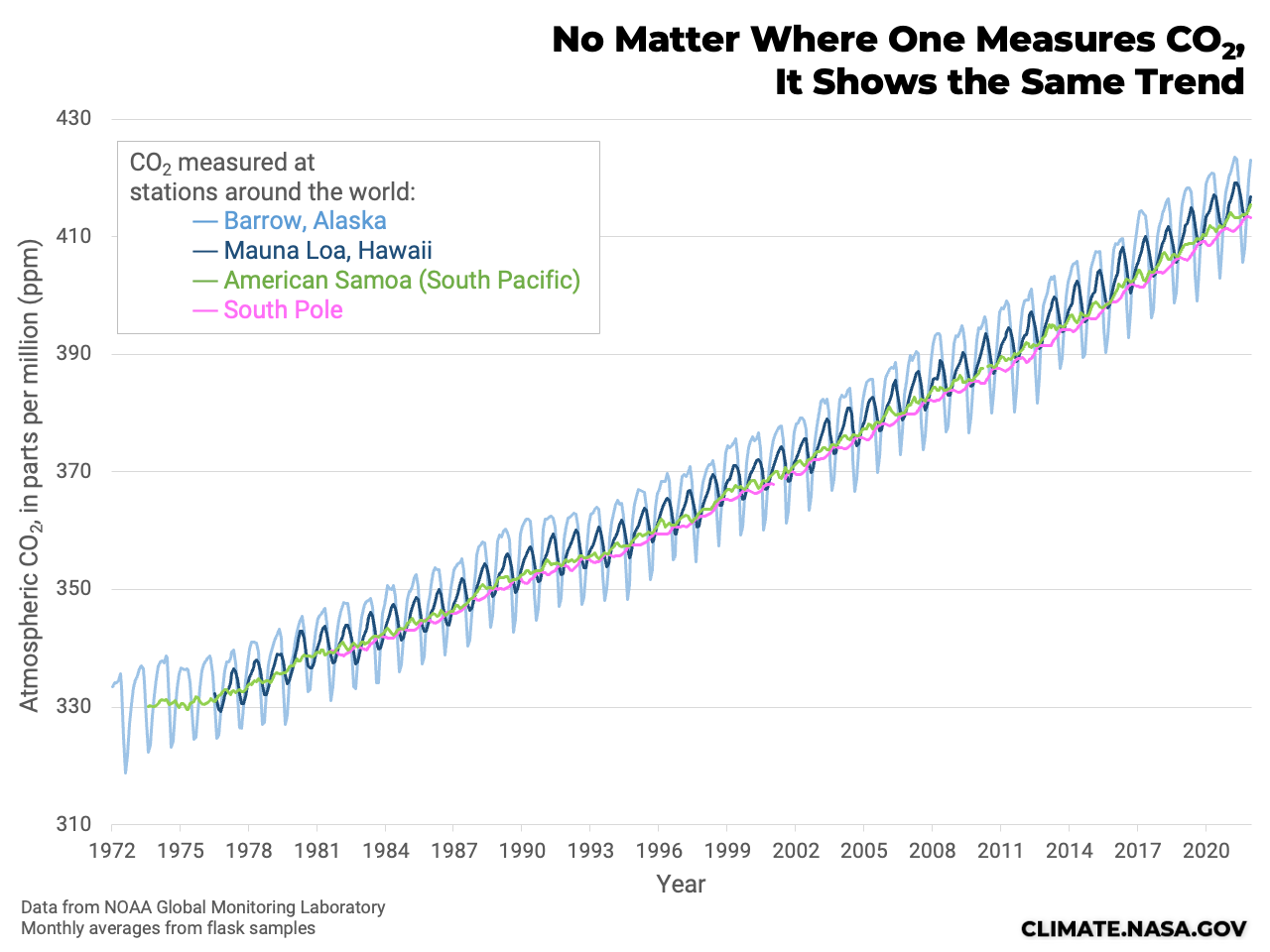
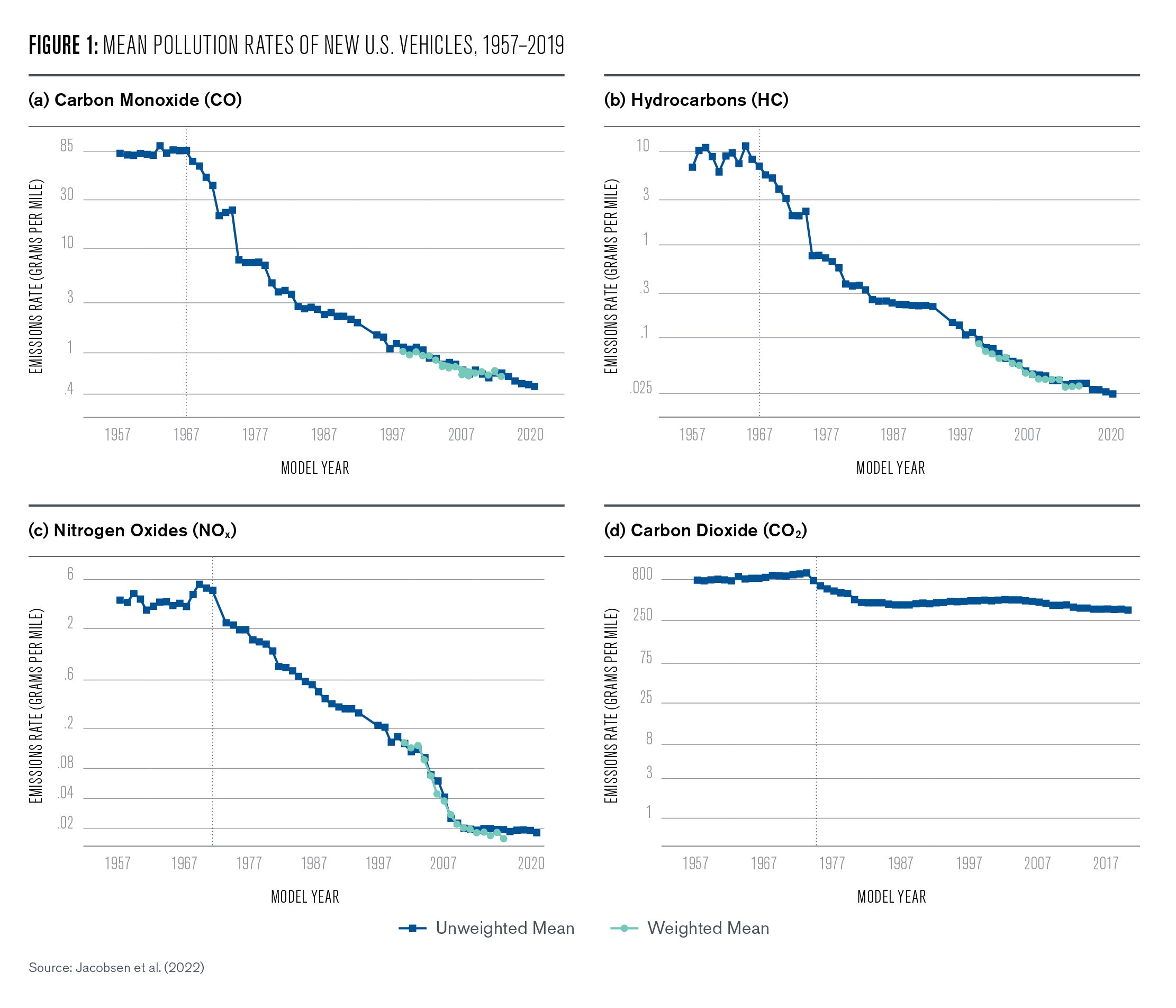
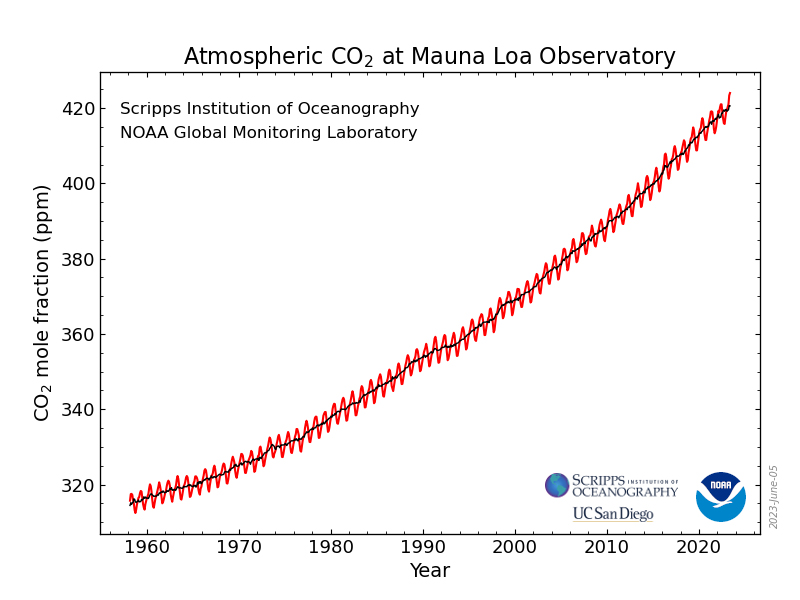
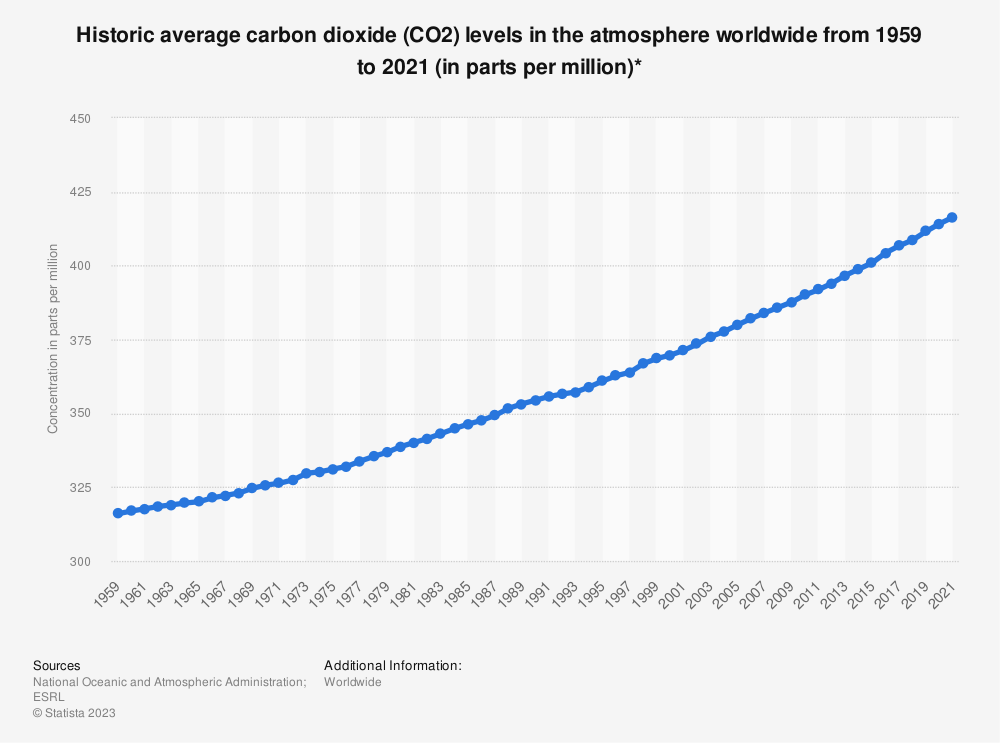
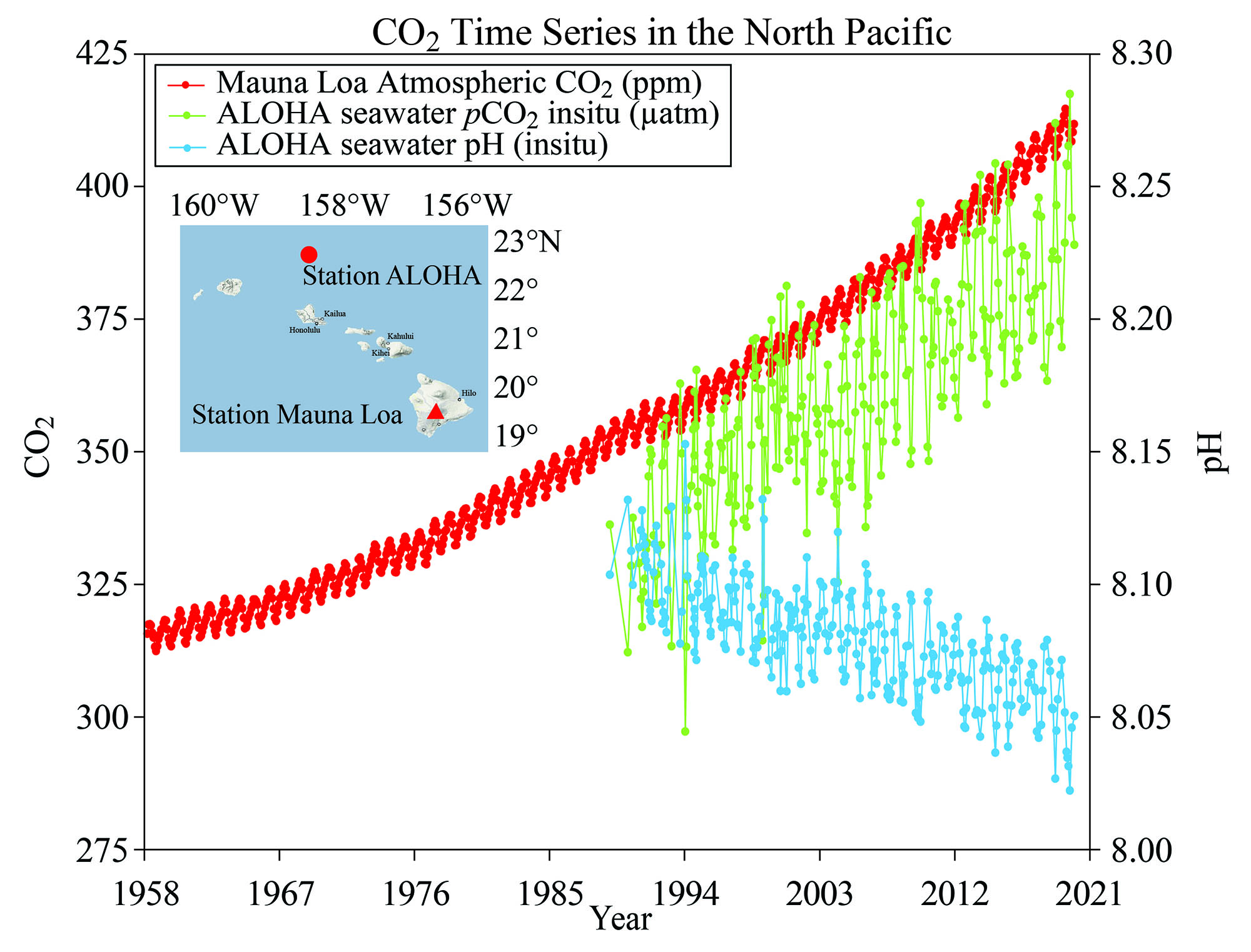
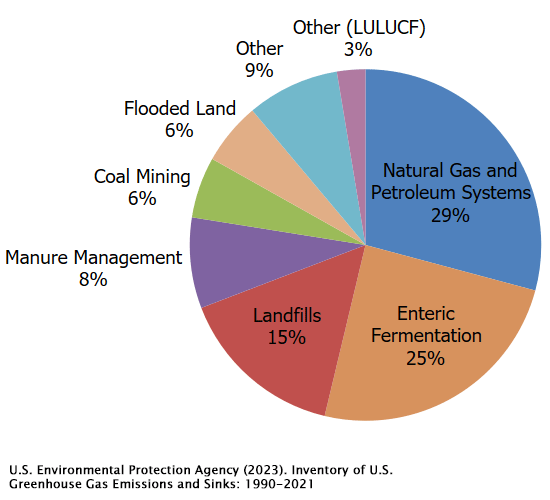
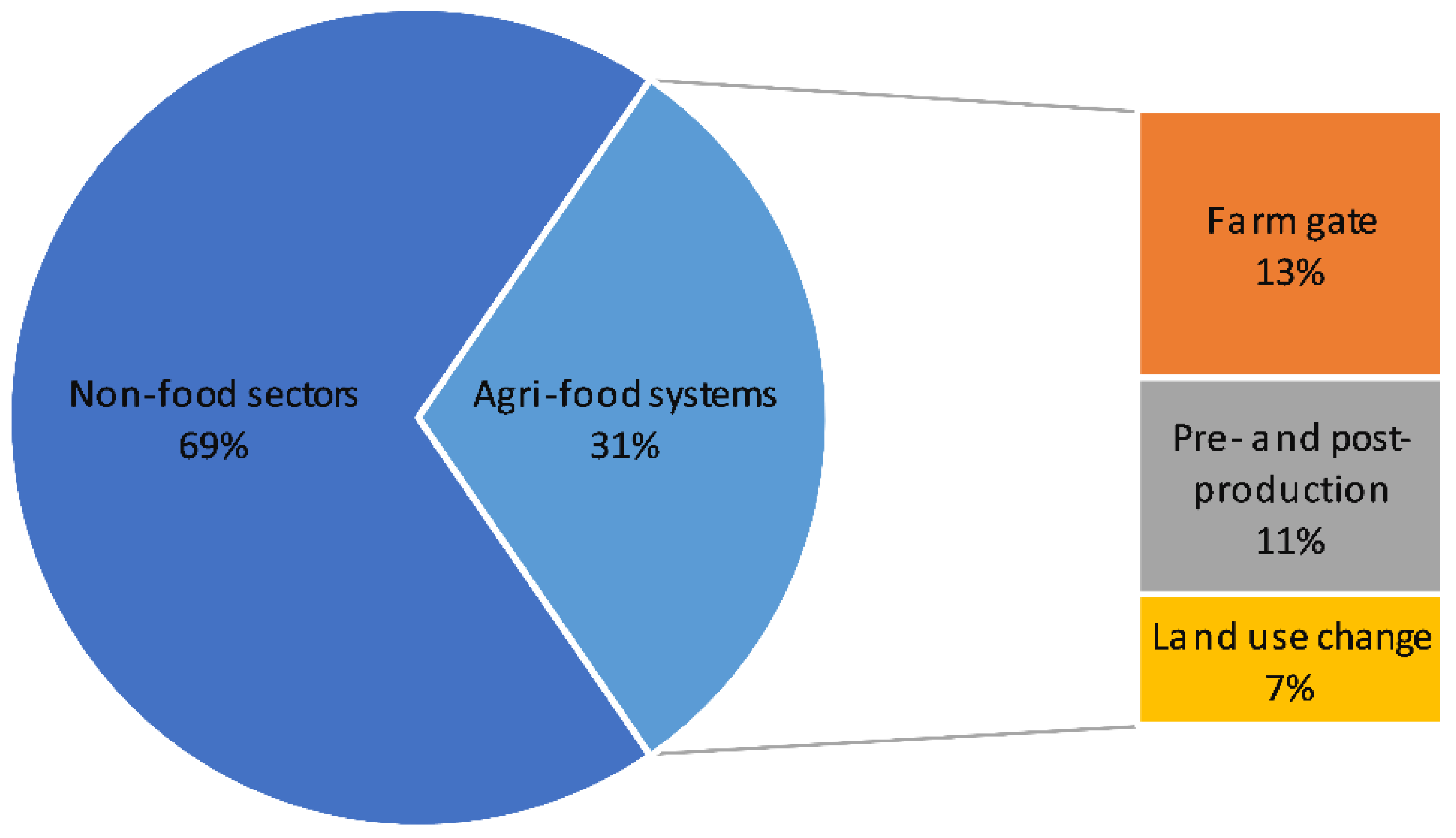
This interactive line graph, map, and data table show the global annual concentration of CO2 in the atmosphere over time. The line graph can be interacted with to compare these parameters for any country or continent. July 4 fireworks emit the equivalent of 50,000 metric tons of carbon dioxide into the atmosphere. That’s a lot, but it’s still small potatoes in the grand scheme of things — the U.S. emits Study with Quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like What two trends are commonly seen in modern monthly CO2 concentration charts?, CO2 levels drop during spring and summer months because __________., Which of the following is true when comparing the Amundsen-Scott South Pole station and Barrow, Alaska CO2 concentration curves? and more. Atmospheric carbon dioxide (CO₂) concentration is measured in parts per million (ppm). Based on the annual analysis from NOAA’s Global Monitoring Lab, global average atmospheric carbon dioxide was 422.8 parts per million (“ppm,” for short) in 2024, a new record high. The increase during 2024 was 3.75 ppm—the largest one-year increase on record. Observed concentrations of carbon dioxide (CO2) in the atmosphere have exceeded 416 parts per million (ppm) threshold at the end of 2021. This is a wakeup call about the constantly rising levels of this greenhouse gas, which is released into the atmosphere by fossil fuel burning and other human activities and is the main driver of climate change. The data contains concentrations of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere from hundreds of thousands of years ago through 2021, measured in parts per million (ppm). The data come from a variety of historical ice core studies and recent air monitoring sites around the world. The modern record of atmospheric carbon dioxide levels began with observations recorded at Mauna Loa Observatory in Hawaii. This graph shows the station's monthly average carbon dioxide measurements since 1958 in parts per million (ppm). GML conducts research on greenhouse gas and carbon cycle feedbacks, changes in aerosols, and surface radiation, and recovery of stratospheric ozone. The first graph shows atmospheric CO 2 levels measured by NOAA at Mauna Loa Observatory, Hawaii, since 1958. The second graph shows CO 2 levels during Earth’s last three glacial cycles, as captured by air bubbles trapped in ice sheets and glaciers. Global CO2 emissions from fossil fuels and land use change How have global emissions of carbon dioxide (CO2) from fossil fuels and land use changed over time? We see that while emissions from fossil fuels have increased, emissions from land use change have declined slightly in recent years. Earth’s atmosphere now has more carbon dioxide in it than it has in millions — and possibly tens of millions — of years, according to data released Thursday by the National Oceanic and The heated rock recombines into silicate minerals, releasing carbon dioxide. When volcanoes erupt, they vent the gas to the atmosphere and cover the land with fresh silicate rock to begin the cycle again. At present, volcanoes emit between 130 and 380 million metric tons of carbon dioxide per year. Study with Quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like Use this graph to rank the sources of anthropogenic CO2 in 2010 based on their relative contribution., The images above show the change in the number of days of the year during which melting occurred in Greenland in 1979-2007 (left) and 2012 (right). What are consequences of this change? Choose one or more: - lower sea level Atmospheric CO 2 concentration measured at Mauna Loa Observatory in Hawaii from 1958 to 2023 (also called the Keeling Curve). The rise in CO 2 over that time period is clearly visible. The concentration is expressed as μmole per mole, or ppm. In Earth's atmosphere, carbon dioxide is a trace gas that plays an integral part in the greenhouse effect, carbon cycle, photosynthesis and oceanic CO2.Earth connects the general public with the latest data and information for stabilizing earth's atmosphere, climate and living environments. Daily CO2 readings are updated here automatically with the latest atmospheric CO2 readings available from the Mauna Loa Observatory in Hawaii. Last update: 3:10:03 AM on Jul. 2, 2025, Hawaii local time (UTC -10) Why does the graph show us? Continual updates of daily CO2 levels recorded at the Mauna Loa Observatory in Hawaii. The graphs show monthly mean carbon dioxide globally averaged over marine surface sites. The Global Monitoring Laboratory has measured carbon dioxide and other greenhouse gases for several decades at a globally distributed network of air sampling sites [Conway, 1994]. The last four complete years plus the current year are shown on the first graph. All years since 1980 are shown on the second If you have looked at the Keeling curve for carbon dioxide concentration that I have shown in past blog postings, you may be wondering why there is a yearly cycle in the concentration of carbon dioxide. The graph below shows the last two years of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere, as measured on Mauna Loa in Hawaii. Human emissions of carbon dioxide and other greenhouse gases are the primary drivers of the global rise in temperatures.1 This link between global temperatures and greenhouse gas concentrations – especially CO2 – has been true throughout Earth’s history.2 In the chart, we see the global average temperature relative to a baseline, which is the average between 1861 and 1890. This gives us
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |