Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
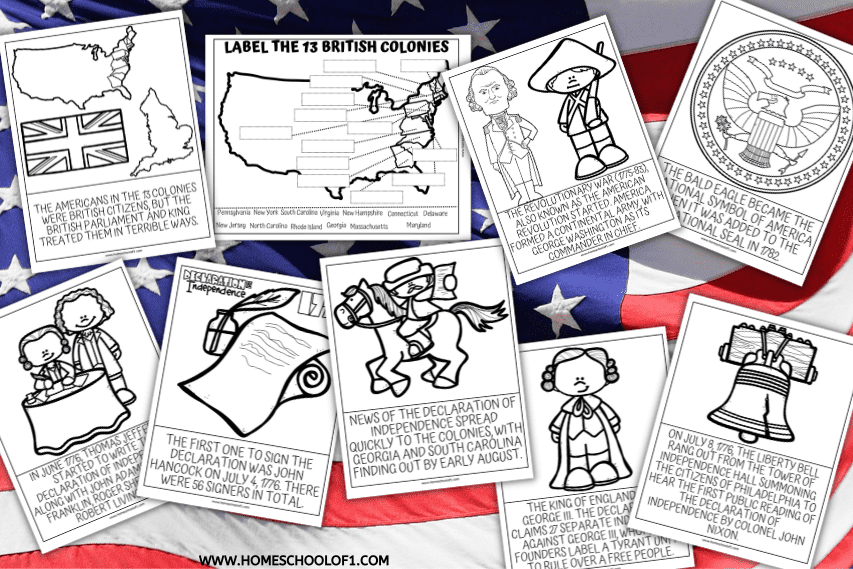
The Declaration of Independence states the principles on which our government, and our identity as Americans, are based. Unlike the other founding documents, the Declaration of Independence is not legally binding, but it is powerful. We will discuss two principles of paramount significance: 1) The truth that our rights come from God; and 2) the reality that political power springs from the People and exists for the purpose of securing their God-given rights. Nearly every printed or manuscript edition of the Declaration of Independence has slight differences in punctuation, capitalization, and even wording. To find out more about the diverse textual tradition of the Declaration, check out our Which Version is This, and Why Does it Matter? resource. Drafted primarily by Thomas Jefferson, it announced the independence of the 13 Original Colonies from British rule. The document laid out the principles of individual rights and self-government, arguing that all people are entitled to “life, liberty, and the pursuit of happiness.” The preamble to the Declaration of Independence outlines the principles upon which the new government would be based. Which of these best describes one of those principles? 13a. The Declaration of Independence and Its Legacy "When in the Course of human events, it becomes necessary for one people to dissolve the political bands which have connected them with another, and to assume among the powers of the earth, the separate and equal station to which the Laws of Nature and of Nature's God entitle them, a decent respect to the opinions of mankind requires that The Declaration of Independence, which oficially broke all political ties between the American colonies and Great Britain, set forth the ideas and principles behind a just and fair government, and the Constitution outlined how this government would function. On the 25th of June, a declaration of the deputies of Pennsylvania, met in provincial conference, expressing their willingness to concur in a vote declaring the United Colonies free and independent States, was laid before Congress and read. The Declaration of Independence is one of our nation's most important founding documents, expressing the basic purposes of self-government, limited constitutionalism, and what it means to be an American. The Declaration of Independence states three basic ideas: (1) God made all men equal and gave them the rights of life, liberty, and the pursuit of happiness; (2) the main business of government is to protect these rights; (3) if a government tries to withhold these rights, the people are free to revolt and to set up a new government. The English Bill of Rights, which influenced the Declaration of Independence, established the idea that A. the power of kings and queens was limited. B. only the chosen leader should make laws. C. a government should not hold free elections. D. people have no right to free speech. The unanimous Declaration of the thirteen united States of America, When in the Course of human events, it becomes necessary for one people to dissolve the political bands which have connected them with another, and to assume among the powers of the earth, the separate and equal station to which the Laws of Nature and of Nature's God entitle The Continental Congress adopted the Declaration of Independence on July 4, 1776. It was engrossed on parchment and on August 2, 1776, delegates began signing it. The Declaration of Independence and the Constitution are cornerstones of American democracy, embodying fundamental ideals that continue to shape the nation. The Declaration emphasizes natural rights, equality, and the right to revolt, establishing a framework for a government accountable to its people. The Constitution builds on these principles with mechanisms like separation of powers On July 4, 1776, the United States officially declared its independence from the British Empire when the Second Continental Congress adopted the Declaration of Independence. The Declaration was authored by a “Committee of Five”—John Adams, Benjamin Franklin, Thomas Jefferson, Robert Livingston, and Roger Sherman—with Jefferson as the main drafter. The Declaration of Independence was based on these principles of government. What are the principles of government described in the book the Two Treatises of Government. 1. The people possess the rights to life, liberty, and property. 2. The government's purpose is to protect peoples rights. 3. The ability to choose reflected the ideals of government by consent argued for in the Declaration. Together, these documents demonstrate that the United States was founded uniquely upon a set of principles and ideals. The principles of the Declaration of Independence informed the creation of the new government under the Constitution. On July 4, 1776, the United States officially declared its independence from the British Empire when the Second Continental Congress adopted the Declaration of Independence. The Declaration was authored by a “Committee of Five”—John Adams, Benjamin Franklin, Thomas Jefferson, Robert Livingston, and Roger Sherman—with Jefferson as the main drafter. But writing to Henry Lee in 1825 The Declaration of Independence The Want, Will, and Hopes of the People Declaration text | Rough Draft | Congress's Draft | Compare | Dunlap Broadside | Image | Scan The Declaration of Independence lays out the core ideals behind and the political philosophy of the United States. The U.S. Constitution creates practical structures and rules both for the federal government and state governments.
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |