Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
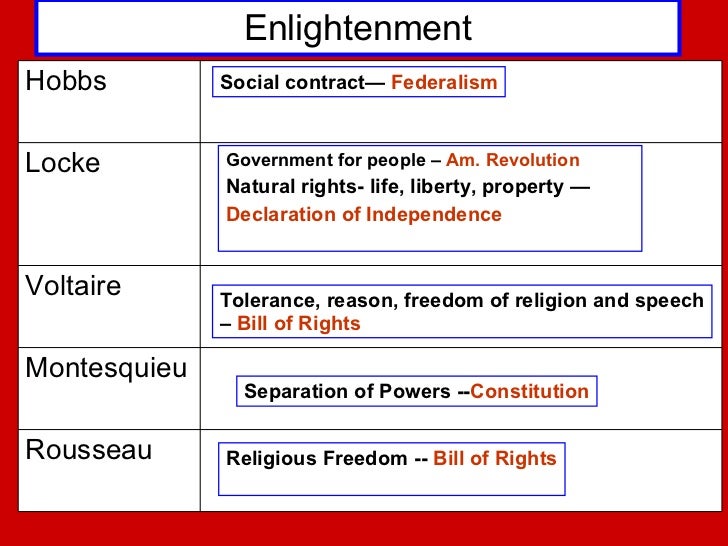
We explore how the Declaration influenced the drafting of the Constitution itself; the abolitionist movement and Abraham Lincoln’s conception of a new birth of freedom after the Civil War; the Seneca Falls Convention and the campaign for women’s suffrage; the Progressive movement and the New Deal; Dr. King and the Civil Rights revolution; throug Rousseau’s ideas in Social Contract heavily influenced the Declaration of Independence. He claimed that people would give up unlimited freedom for the security provided by a government, but also that people of the state hold ultimate right to power. Consider the document that inspired the Declaration of Independence: the Virginia Declaration of Rights, penned primarily by George Mason and adopted by Virginia’s Constitutional Convention in Thomas Jefferson used the thoughts first penned by John Locke while writing the Declaration of Independence. The phrase "life, liberty, and pursuit of happiness," was an idea first considered by Locke in his Two Treatises on Government. His most famous writings, A Letter Concerning Toleration and Second Treatise of Government, both heavily influenced the author of the Declaration of Independence, Thomas Jefferson. Many believe much of the most memorable language of the Declaration of Independence is derived from Locke’s works. Written primarily by Thomas Jefferson, it explains why the Thirteen Colonies decided to separate from Great Britain during the American Revolution (1765-1789). It was adopted by the Second Continental Congress on 4 July 1776, the anniversary of which is celebrated in the US as Independence Day. Authored primarily by Thomas Jefferson, the Declaration is a powerful statement on the principles of liberty, equality, and popular sovereignty. This study module will explore the historical context, philosophical influences, political significance, and the enduring legacy of the Declaration of Independence. Thomas Jefferson, a prominent statesman and philosopher, was entrusted with drafting the Declaration of Independence. His eloquent writing style and profound understanding of Enlightenment ideals allowed him to articulate the colonies’ aspirations for liberty and governance. These three documents, known collectively as the Charters of Freedom, have secured the rights of the American people for more than two and a quarter centuries and are considered instrumental to the founding and philosophy of the United States. Declaration of Independence Learn More The Declaration of Independence expresses the ideals on which the United States was founded and the reasons for Several key Enlightenment concepts directly influenced the drafting of the Declaration. These include: Natural Rights: Philosophers like John Locke posited that individuals possess inherent rights that predate and transcend governmental authority. These rights are unalienable, meaning they cannot be legitimately surrendered or revoked. Enlightenment Thinkers and Their Core Ideas John Locke, often credited as the father of modern republican government, had a profound impact on the American Founding Fathers. Locke's theory of natural rights argued that every individual is entitled to life, liberty, and property, principles woven into the Declaration of Independence. He proposed that a legitimate government [] The influence of the Enlightenment on the Declaration of Independence is undeniable. The Declaration, born from the intellectual ferment of the 18th century, articulated principles that continue to shape our understanding of freedom, equality, and self-government. The Declaration of Independence was written largely by Jefferson, who had displayed talent as a political philosopher and polemicist in his A Summary View of the Rights of British America, published in 1774. John Locke’s political theory directly influenced the U.S. Declaration of Independence in its assertion of natural individual rights and its grounding of political authority in the consent of the governed. Locke also advocated a separation of executive, legislative, and judicial powers, a feature of the form of government established in the U.S. Constitution. Declaration of Rights: Outlines the political ideas based on natural rights, reflecting Locke's influence. List of Complaints: Enumerates grievances against King George III, justifying the colonies' decision to break away. Explore Thomas Jefferson's influences in writing the Declaration of Independence, John Locke, Montesquieu, and the Magna Carta The Declaration of Independence was heavily influenced by Enlightenment thinkers, particularly John Locke. It reflects Enlightenment ideals such as human rights, equality, and the social contract. Which philosopher influenced the authors of the Declaration of Independence? John Locke John Locke an English Philosopher, who believed that the three purposes of Government were life, liberty and property. He believed that common people could have some degree of control over their government Study with Quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like A purpose of the Declaration of Independence was to explain A. the problems the colonists had with British rule. B. the reasons colonists formed the Continental Congress. C. why some colonists refused to boycott British goods. D. why the colonies had the Boston Tea Party., The English Bill of Rights, which influenced the Thomas Jefferson is considered the primary author of the Declaration of Independence, although Jefferson's draft went through a process of revision by his fellow committee members and the Second Continental Congress.
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |