Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
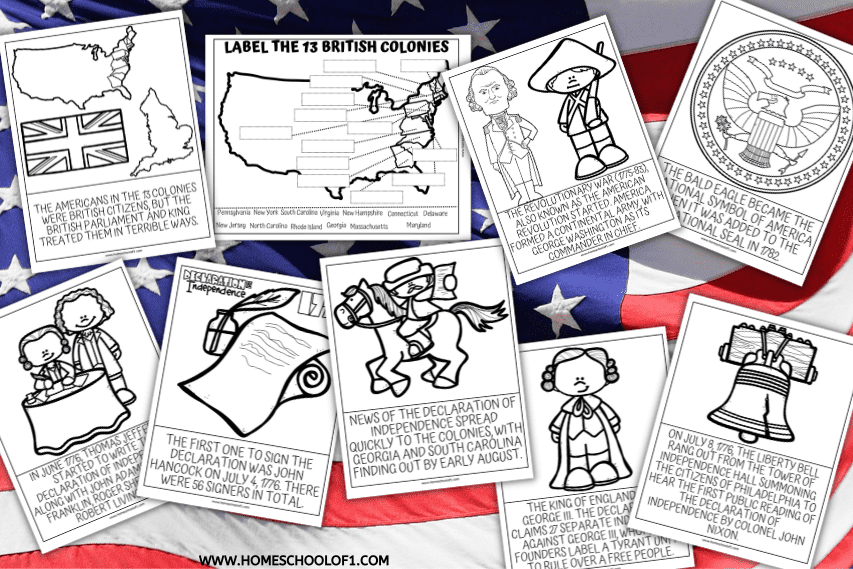
Ms. Hamilton, a Ph.D. in English from Berkeley, died in 2013. This article, posted on HNN in 2008, was originally published under the title, "The Surprising Origins and Meaning of the 'Pursuit of “The pursuit of happiness” is the most famous phrase in the Declaration of Independence. Conventional history and popular wisdom attribute the phrase to the genius of Thomas Jefferson when "Life, Liberty, and the Pursuit of Happiness" In this activity, students discuss some of the ideals in the Declaration of Independence. Form small groups to discuss the meaning of the three natural rights that Jefferson identified in the Declaration of Independence: "Life, Liberty, and the Pursuit of Happiness." unalienable Rights, that among these are Life, Liberty, and the Pursuit of Happiness . . . .” —The Declaration of Independence, 1776. One of the most famous lines from the Declaration of Independence is, “Life, liberty and the pursuit of Happiness.” It used by numerous Americans to represent what this country stands for. For instance, the Virginia Declaration of Rights—written mainly by George Mason and adopted on June 12, 1776—speaks of “the enjoyment of life and liberty, with the means of acquiring and Borrowing the idea of pursuing virtue or happiness from Scottish moral philosophers, such as Henry Home, Lord Kames, Jefferson went so far as to substitute the phrase "the pursuit of happiness" for the word "property" in his litany of inalienable natural rights. Where did this idea come from? These rights, as spelled out in the Declaration of Independence are life, liberty, and the pursuit of happiness. These three rights are taken directly from a work of John Locke's titled Two Alan Ryan (1965) argued that since property for Locke includes life and liberty as well as estate (Two Treatises 2.87), even those without land could still be members of political society. The dispute between the two would then turn on whether Locke was using “property” in the more expansive sense in some of the crucial passages. Study with Quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like Which of the following are the inalienable rights referred to in the Declaration of Independence? a. life, liberty, and property b. life, liberty, and the pursuit of happiness c. life, respect, and equal protection d. liberty, health, and community e. honor, liberty, and peace Feedback, The legislative branch of the federal He was almost certainly influenced by George Mason's Virginia Declaration of Rights (adopted June 12, 1776), which referred to "the enjoyment of life and liberty, with the means of acquiring and possessing property, and pursuing and obtaining happiness and safety." The Declaration's most famous sentence reads: "We hold these truths to be self-evident, that all men are created equal; that they are endowed by their Creator with certain unalienable rights; that among these are life, liberty, and the pursuit of happiness." The unanimous Declaration of the thirteen united States of America, When in the Course of human events, it becomes necessary for one people to dissolve the political bands which have connected them with another, and to assume among the powers of the earth, the separate and equal station to which the Laws of Nature and of Nature's God entitle Study with Quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like the idea that government should be restricted in its lawful uses of power and hence in its ability to deprive people of their liberty is expressed by the term: - federalism - self-government - judicial review - limited government - natural rights, _________ was the primary author of the Declaration of Independence - John Locke The second paragraph of the Declaration of Independence begins with perhaps its most famous line. “We hold these truths to be self-evident, that all men are created equal, that they are endowed by their Creator with certain unalienable Rights, that among these are Life, Liberty and the pursuit of Happiness.” This statement echoed the writings of English philosopher John Locke. Locke The Declaration of Independence states the principles on which our government, and our identity as Americans, are based. Unlike the other founding documents, the Declaration of Independence is not legally binding, but it is powerful. an English Philosopher, who believed that the three purposes of Government were life, liberty and property. He believed that common people could have some degree of control over their government Nearly every printed or manuscript edition of the Declaration of Independence has slight differences in punctuation, capitalization, and even wording. To find out more about the diverse textual tradition of the Declaration, check out our Which Version is This, and Why Does it Matter? resource. Our forefathers understood the outcome of tomorrow is a direct result of the actions taken today. Ratified on July 4, 1776, The Declaration of Independence offers the unalienable rights of life, liberty and the pursuit of happiness (or property) to all Americans. John Locke had such a profound influence on Thomas Jefferson that he may be deemed an honorary founding father of the United States. He advocated the natural equality of human beings, their natural rights to life, liberty, and property, and defined legitimate government in terms that Jefferson would later use in the Declaration of Independence. We hold these truths to be self-evident, that all men are created equal, that they are endowed by their Creator with certain unalienable Rights, that among these are Life, Liberty and the pursuit of Happiness. That to secure these rights, Governments are instituted among Men, deriving their just powers from the consent of the governed.
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |